An interior gateway protocol or IGP such as RIP, or OSPF is basically any routing protocol running within an Autonomous System. The routing information or prefixes exchanged within the various Autonomous Systems can be used to populate the Layer 3 routing tables.
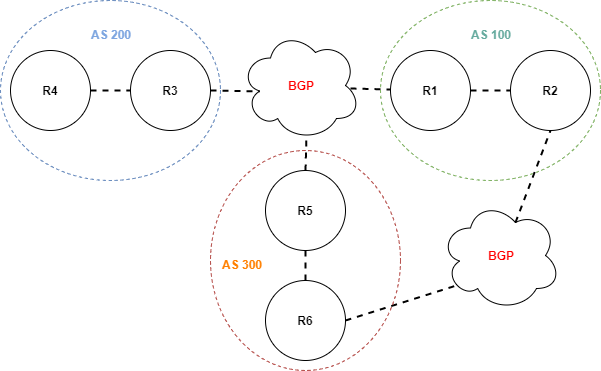
There are several ways to inject routes into BGP, one is via the network statement, and the other is via redistribution. There are also several ways to use a Route Map to control which prefixes get advertised. One is in conjunction with the neighbor statement, the other is in conjunction with the network and or redistribution statement.
Lets get started with the configuration of R1’s Route Maps and Prefix Lists
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#ip prefix-list RIP seq 5 permit 192.168.0.0/24
R1(config)#ip prefix-list RIP seq 10 permit 192.168.1.0/24
R1(config)#
Now that the prefix list have been created lets create the Route Maps and associate the Prefix Lists.
R1(config)#route-map AS200 permit 10
R1(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list RIP
R1(config-route-map)#exit
R1(config)#route-map AS300 permit 10
R1(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list RIP
R1(config-route-map)#exit
R1(config)#
Next lets move into the BGP configuration on router R1.
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#no synchronization
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 10.0.0.1
R1(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes
R1(config-router)#redistribute rip
R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 200
R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.0.2 route-map AS200 out
R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.1.2 remote-as 300
R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.1.2 route-map AS300 out
R1(config-rotuer)#neighbor 172.16.0.2 remote-as 100
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#
Now lets get started with our first IGP RIP. Let’s get it up and running on Router R1
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#exit
R1#
Lets take a quick look at Router R1’s RIP database
R1#show ip rip database
172.16.0.0/16 auto-summary
172.16.0.0/30 directly connected, Ethernet1/0
192.168.0.0/24 auto-summary
192.168.0.0/24 directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.1.0/24 auto-summary
192.168.1.0/24
[1] via 172.16.0.2, 00:00:01, Ethernet1/0
Now lets jump into router R2’s iBGP and eBGP configuration
R2#configure terminal
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#no synchronization
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 172.16.0.2
R2(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes
R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.1 remote-as 300
R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.1 send-community
R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.1 route-map AS300 out
R2(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.0.1 remote-as 100
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#
Lets get router R2’s IGP configuration up and running
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#version 2
R2(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#exit
R2#
Lets take a look at the RIP database on R2
R2#show ip rip database
172.16.0.0/16 auto-summary
172.16.0.0/30 directly connected, Ethernet0/0
192.168.0.0/24 auto-summary
192.168.0.0/24
[1] via 172.16.0.1, 00:00:27, Ethernet0/0
192.168.1.0/24 auto-summary
192.168.1.0/24 directly connected, Loopback0
R1#show ip bgp summary
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.0.2 4 200 94 94 8 0 0 01:29:49 2
10.0.1.2 4 300 92 94 8 0 0 01:29:54 0
172.16.0.2 4 100 92 96 8 0 0 01:29:50 0
R#show ip bgp summary
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.6.1 4 300 88 94 11 0 0 01:25:32 0
172.16.0.1 4 100 92 88 11 0 0 01:25:29 7
Lets configure the Route Maps and Prefix Lists for R3
R3#configure terminal
R3(config)#ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 5 permit 192.168.2.0/24
R3(config)#ip prefix-list EIGRP seq 10 permit 192.168.3.0/24
R3(config)#
Next will configure the Route Map and associate the prefix list on Router R3.
R3(config)#route-map AS300 permit 10
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list EIGRP
R3(config-route-map)#route-map AS100 permit 10
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list EIGRP
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#
Now lets jump into Router R3 eBGP and iBGP configuration
R3(config)#router bgp 200
R3(config-router)#no synchronization
R3(config-router)#bgp router-id 10.0.0.2
R3(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes
R3(config-router)#redistribute eigrp 200
R3(config-router)neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 100
R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.0.1 route-map AS100 out
R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.2.2 remote-as 300
R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.2.2 route-map AS300 out
R3(config-router)#neighbor 172.17.0.2 remote-as 200
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#
Now we can move on with R3 IGP configuration and get it up and running
R3(config)#router eigrp 200
R3(config-router)#network 172.17.0.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config-router)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.2
R3(config-router)#redistribute eigrp 200
R3(config-router)#end
R3#
Next lets continue with the iBGP configuration on router R4.
R4#configure terminal
R4(config)#router bgp 200
R4(config-router)#no synchronization
R4(config-router)#bgp router-id 172.17.0.2
R4(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes
R4(config-router)#neighbor 172.17.0.1 remote-as 200
R4(config-router)#no auto-summary
R4(config-router)#exit
R4(config)#
Lets get R4’s IGP configuration up and running
R4(config)#router eigrp 200
R4(config-router)#network 172.17.0.0
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
R4(config-router)#no auto-summary
R4(config-router)#eigrp router-id 172.17.0.2
R4(config-router)#end
R4#
R3#show ip bgp summary
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.0.0.1 4 100 26 26 6 0 0 00:21:06 2
10.0.2.2 4 300 24 26 6 0 0 00:21:04 0
172.17.0.2 4 200 24 28 6 0 0 00:21:10 0
R4#show ip bgp summary
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
172.17.0.1 4 200 31 27 7 0 0 00:24:08 5
R3#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(200)/ID(10.0.0.2)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 128256
via Connected, Loopback0
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 409600
via 172.17.0.2 (409600/128256), Ethernet1/0
P 172.17.0.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 281600
via Connected, Ethernet1/0
R4#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(200)/ID(172.17.0.2)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 409600
via 172.17.0.1 (409600/128256), Ethernet0/0
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 128256
via Connected, Loopback0
P 172.17.0.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 281600
via Connected, Ethernet0/0
Next we need to continue our eBGP and iBGP configuration on router R5
R5#configure terminal R5(config)#router bgp 300 R5(config-router)#no synchronization R5(config-router)#bgp router-id 10.0.1.2 R5(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.1.1 remote-as 100 R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.1.1 route-map AS100 out R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.2.1 remote-as 200 R5(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.2.1 route-map AS200 out R5(config-router)#neighbor 172.18.0.2 remote-as 300 R5(config-router)#no auto-summary R5(config-router)#exit R5(config)#
Lets configure R5’s Route Map and Prefix Lists
R5(config)#ip prefix-list OSPF seq 5 permit 192.168.4.0/24 R5(config)#ip prefix-list OSPF seq 10 permit 192.168.5.0/24 R5(config)#
Next we can move into the Route Map configuration on router R5
R5(config)#route-map AS200 permit 10 R5(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list OSPF R5(config-route-map)#exit R5(config)#route-map AS100 permit 10 R5(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list OSPF R5(config-route-map)#exit R5(config)#
Moving on now… Lets configure router R5’s IGP OSPF configuration
R5(config)#router ospf 300 R5(config-router)#router-id 172.18.0.1 R5(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes R5(config-router)#network 172.18.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R5(config-router)#network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R5(config-router)#end R5#
Next lets get router R6’s iBGP and eBGP configuration up and running
R6#configure terminal R6(config)#router bgp 300 R6(config-router)#no synchronization R6(config-router)#bgp router-id 172.18.0.2 R6(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes R6(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.2 remote-as 100 R6(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.2 send-community R6(config-router)#neighbor 10.0.6.2 route-map AS100 out R6(config-router)#neighbor 172.18.0.1 remote-as 300 R6(config-router)#no auto-summary R6(config-router)#exit R6(config)#
Lets get R6’s IGP OSPF configuration up and running
R6(config)#router ospf 300 R6(config-router)#router-id 172.18.0.2 R6(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes R6(config-router)#network 172.18.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R6(config-router)#network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R6(config-router)#exit R6(config)#
Lets configure R6’s Route Map and Prefix List and Community with R1
R6(config)#route-map AS100 permit 10 R6(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list OSPF R6(config-route-map)#set community 300:100 R6(config-route-map)#end R6#
R5#show ip bgp summary Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.0.1.1 4 100 46 44 5 0 0 00:41:56 2 10.0.2.1 4 200 46 44 5 0 0 00:41:55 2 172.18.0.2 4 300 45 48 5 0 0 00:41:56 1
R5#show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID (172.18.0.1) (Process ID 300) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count 172.18.0.1 172.18.0.1 754 0x80000003 0x008C1D 2 172.18.0.2 172.18.0.2 735 0x80000003 0x009F06 2 Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum 172.18.0.2 172.18.0.2 735 0x80000002 0x00DA5F
I hope you found this post on BGP Redistribution helpful and informative. Be sure to let me know what you think by leaving suggestions, and feedback in the comments section below. You can find out more about these and other articles be checking out recent posts and archives. To learn more about me be sure to check out the About page. And as always thanks again for visiting The Packet.